Eigenvalues
Contents
6.10. Eigenvalues#
include("smij-functions.jl");
Eigenvalue problems behave similarly to BVPs in many ways.
We warm up with the Mathieu equation,
where \(q\) is a real parameter. The behavior of the eigenvalues as a function of \(q\) is of classical interest for forced oscillations.
Using Fourier differentiation, the natural discretization of the operator on the left-hand side is
Everything is straightforward.
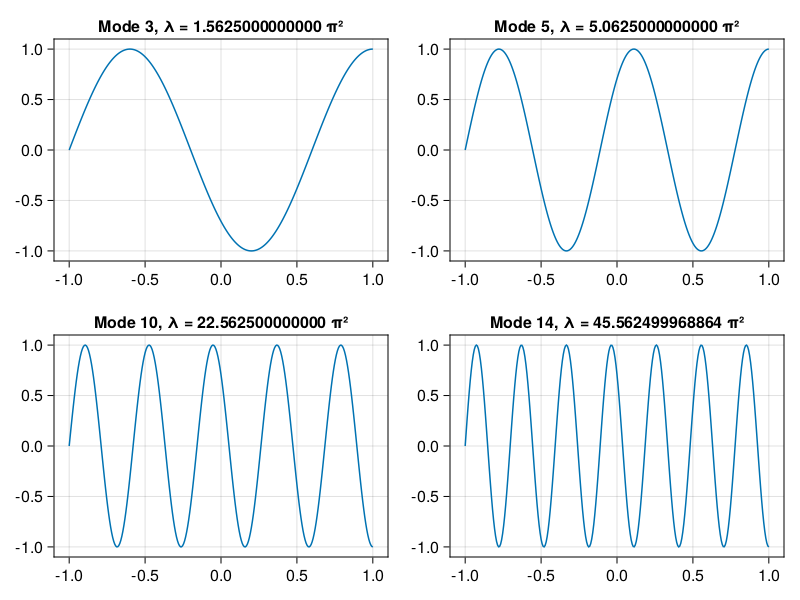
p21: eigenvalues of Mathieu operator#
N = 42
x,D,D² = trig(N)
q = 0:0.1:15
data = zeros(11,0)
for q in q
λ = eigvals(-D² + 2q * diagm(cos.(2x)))
data = [data real(λ[1:11])]
end
using CairoMakie
fig = Figure()
ax = Axis(fig[1,1], xlabel="q", ylabel="λ", yticks=-24:4:32)
lines!(q, data[1,:], color=:black, label="a₀")
series!(q, data[3:2:end, :], color=:Set1, labels=["a"*Char(Int('₀')+n) for n in 1:5])
series!(q, data[2:2:end, :], color=:Set2, labels=["b"*Char(Int('₀')+n) for n in 1:5])
limits!(0, 15, -24, 32)
Legend(fig[1,2], ax)
fig
Generalized eigenproblem#
Next we look at an eigenvalue variant of the Airy equation,
The obvious discretization of the ODE is
Given the boundary conditions, we should lop off the first and last row and column from the above. What’s left is a generalized eigenproblem of the form \(\bfA \bfu = \lambda \mathbf{M} \bfu\). If \(\mathbf{M}\) is invertible, we can just look for ordinary eigenvalues of \(\mathbf{M}^{-1}\bfA\), but since \(0\) might be a grid point, it’s best to solve it as posed above.
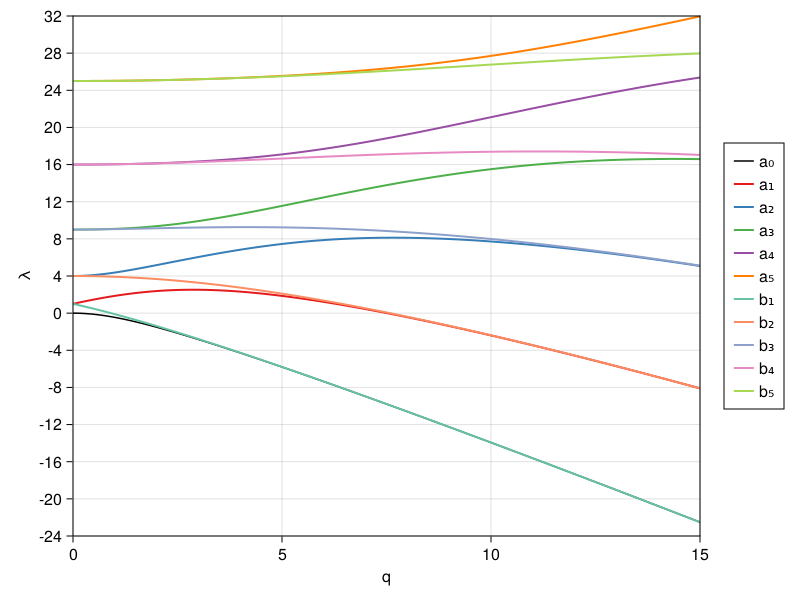
p22: 5th eigenvector of Airy equation#
xx = range(-1,1,301)
N = 12:12:48
VV = zeros(length(xx),length(N))
λλ = zeros(length(N))
for (j,N) in enumerate(N)
D, x = cheb(N)
D² = (D^2)[2:N, 2:N]
λ, V = eigen(D², diagm(x[2:N])) # generalized ev problem
ii = findall(λ .> 0)[5]
λλ[j] = λ[ii]
v = [0; V[:, ii]; 0]
p = polyinterp(x, v)
VV[:,j] = normalize( sign(p(0)) * p.(xx), Inf )
end
using PyFormattedStrings
fig = Figure()
ax = vec( [Axis(fig[j,i]) for i in 1:2, j in 1:2] )
for (j,ax) in enumerate(ax)
lines!(ax,xx,VV[:,j])
ax.title = f"N = {N[j]} λ = {λλ[j]:.14g}"
end
linkyaxes!(ax...)
fig
Neumann condition#
We can also use a generalized eigenproblem to easily impose boundary conditions of types other than Dirichlet. Note that any boundary condition of a linear eigenvalue problem is necessarily homogeneous.
Suppose that \(\bfA\) is the \((N+1)\times(N+1)\) discretization of an ODE over the entire grid. Let the boundary conditions be discretized as a \(2\times(N+1)\) matrix \(\bfB\), so that \(\bfB \bfu = \bfzero\) must be imposed in place of the boundary rows of \(\bfA\). Then
where \(\bfC\) is the \((N-1)\times (N+1)\) matrix that chops off the first and last rows. We use this below to solve the eigenvalue problem
Rather than chopping off rows and then appending a boundary condition matrix, we just overwrite the boundary rows of \(\bfA\) in place with the rows of \(\bfB\). At the left end, it’s a row of the identity matrix, and at the right, it’s a row of \(\bfD_x\).
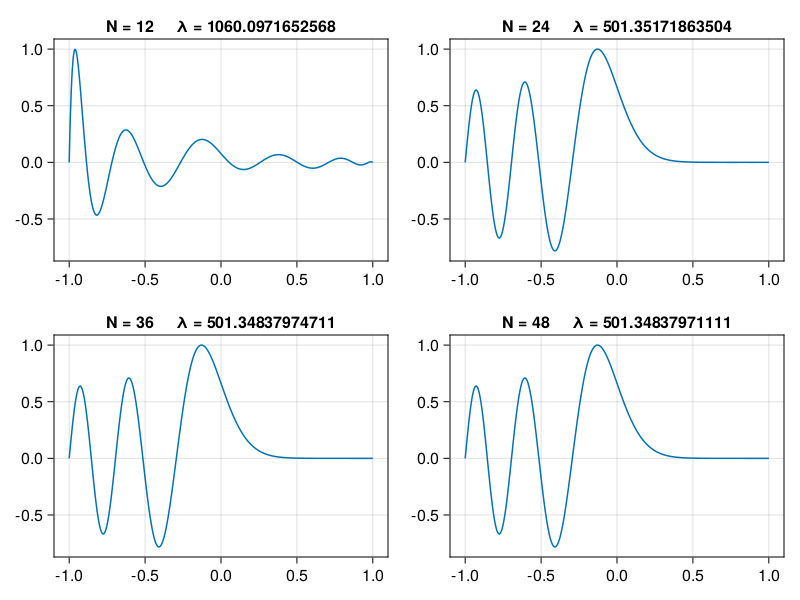
N = 40
D, x = cheb(N)
A = -D^2
A[N+1,:] .= I(N+1)[N+1,:] # Dirichlet at x = -1
A[1,:] .= D[1,:] # Neumann at x = 1
M = diagm([0; ones(N-1); 0])
λ, V = eigen(A,M);
xx = range(-1,1,301)
VV = hcat( [polyinterp(x,v).(xx) for v in eachcol(V[:,1:20])]... );
fig = Figure()
ax = vec( [Axis(fig[j,i]) for i in 1:2, j in 1:2] )
index = [3,5,10,14]
for (i,j) in enumerate(index)
lines!(ax[i], xx, VV[:,j])
ax[i].title = f"Mode {j}, λ = {λ[j]/π^2:#.14g} π²"
end
linkyaxes!(ax...)
fig